Investigation
of the benefits of radar-based sensor technologies for higher autonomy in flight, navigation, landing &. eVTOL ground operations
Analysis
and definition of requirements for take-off procedures and landing procedures of eVTOLs.
Testing
How eVTOLs can be connected to a land system as well as Droniq's Unmanned Traffic Management (UTM) system.
Project duration
Project start: January 2023 Project end: 2025
The goal
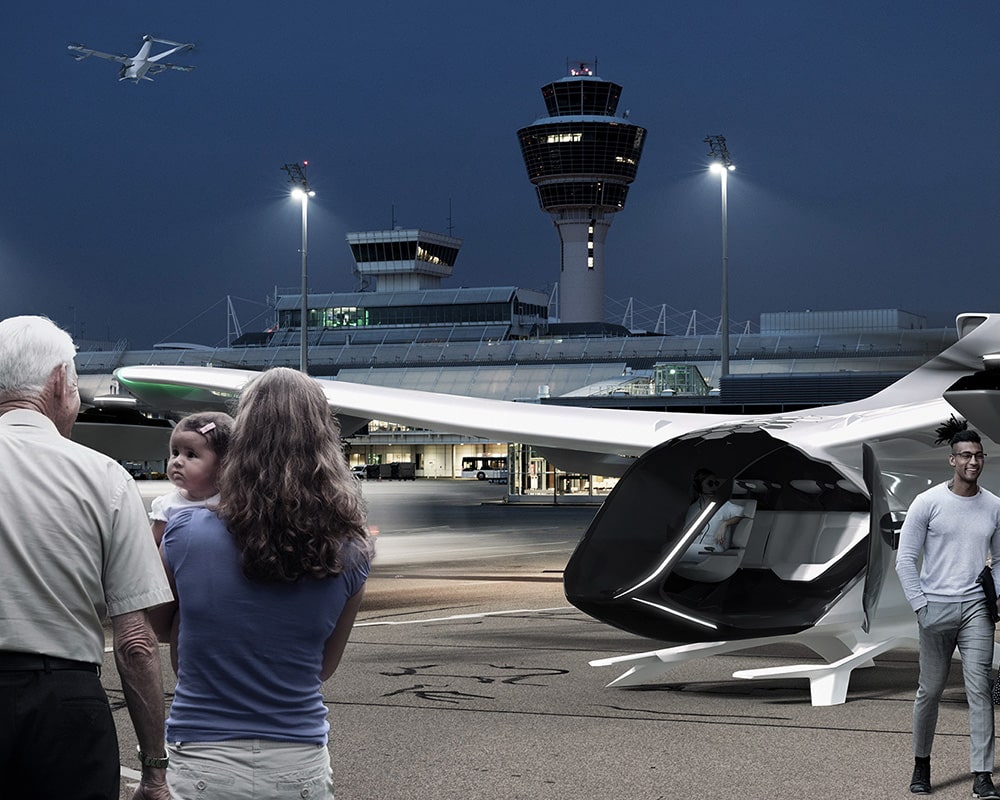
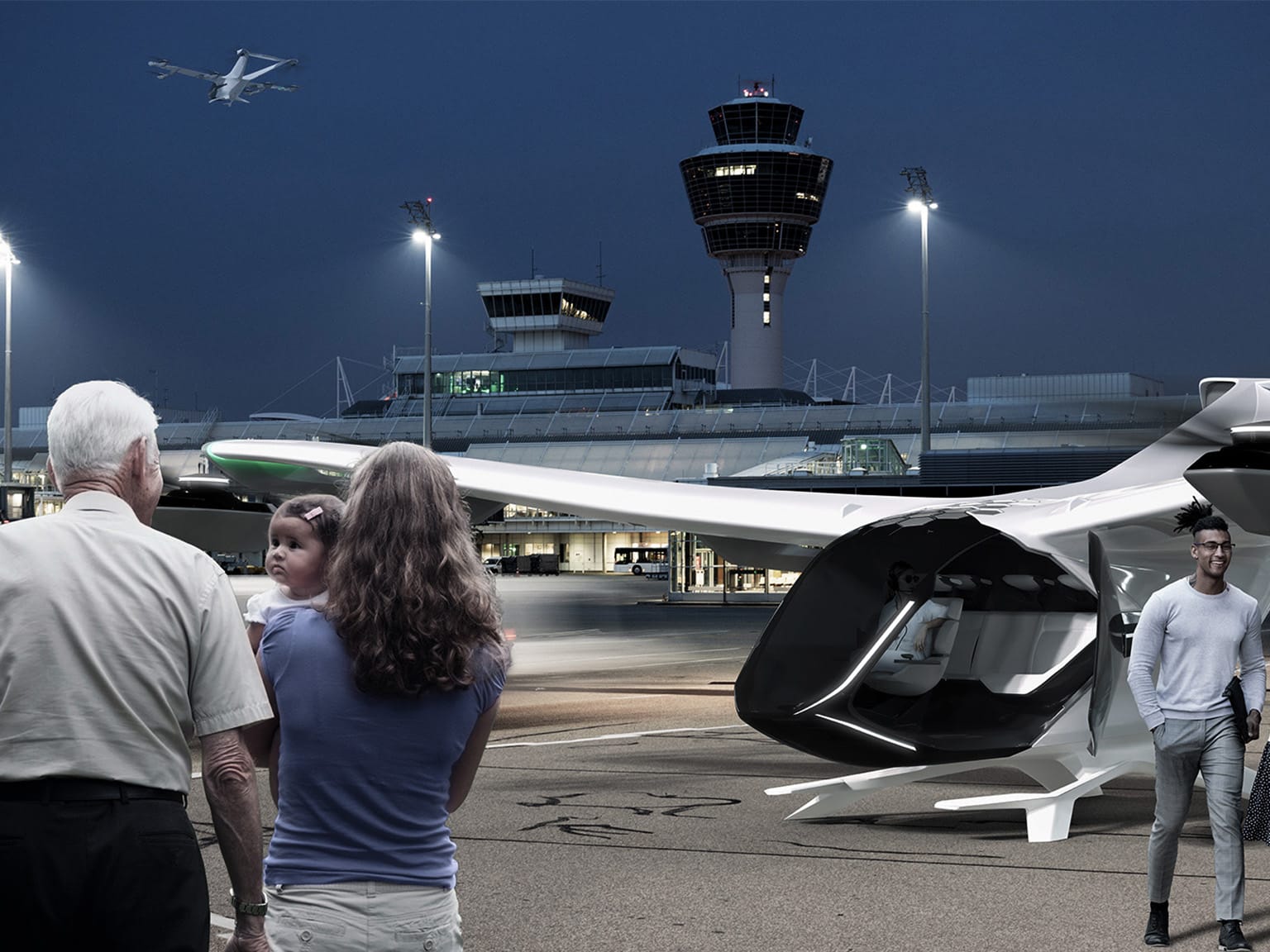
Exploring the benefits of GNSS-independent, local radar-based sensor technology for applications beyond precise positioning
to enhance the safety and efficiency of UAM elements (eVTOL, airspace, and ground infrastructure).
AMI-PGS is part of the AMI initiative (Air Mobility Initiative).

The implementation
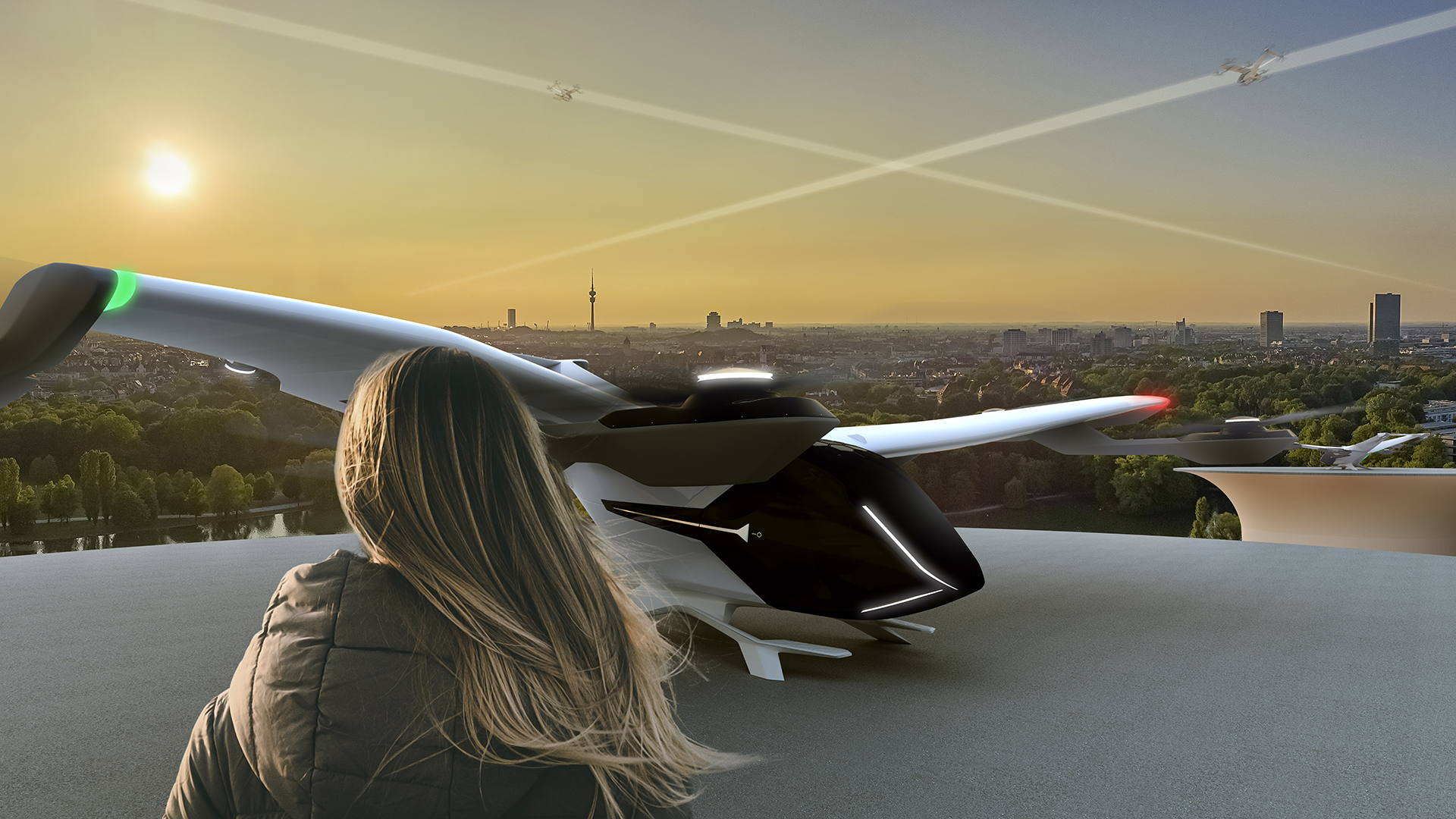
The AMI-PGS project is being implemented in several steps: First, requirements for take-off and landing procedures for eVTOLs are analyzed and defined.
Legal and regulatory framework conditions are also taken into account. The project partners will then design and test various concepts for positioning and managing eVTOLs.
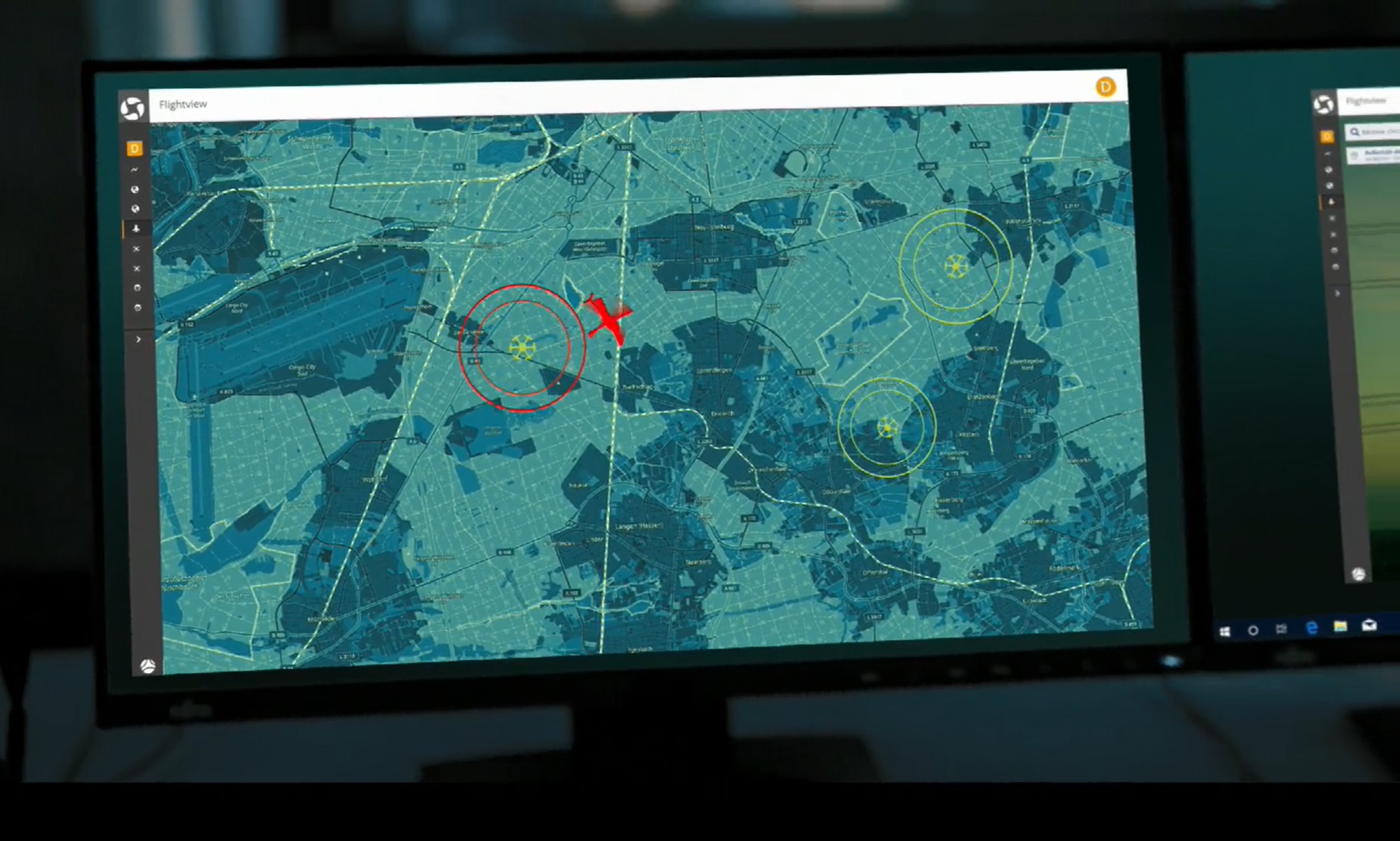
Among other things, the connection to a UTM system that enables the flow of information between the eVTOLs and other air traffic participants is being investigated as part of this.

Our contribution
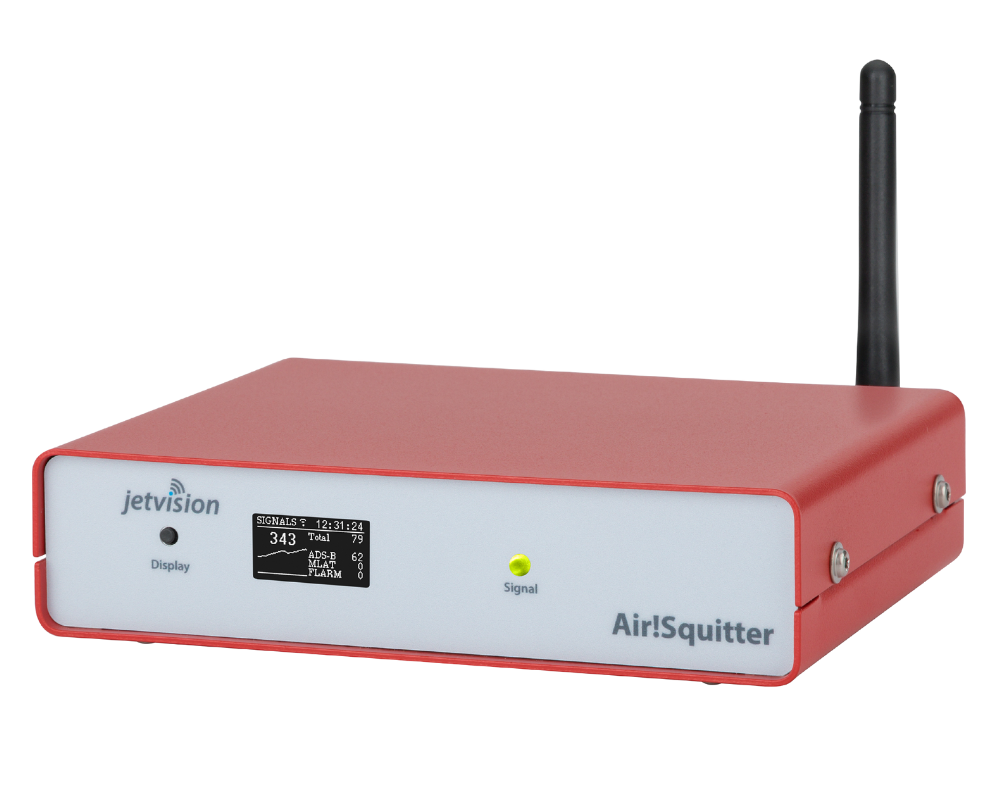
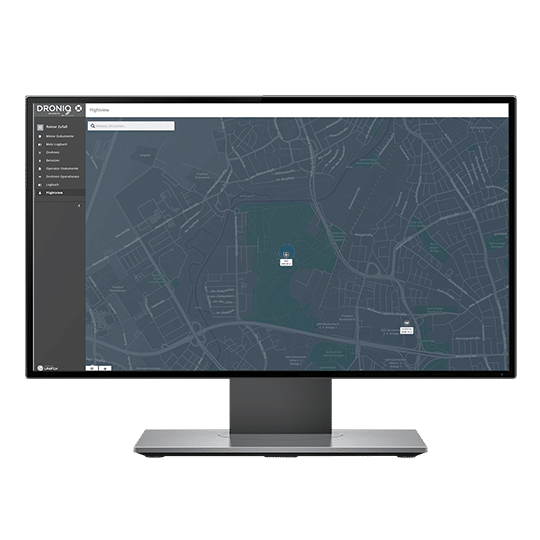
As part of the AMI-PGS project, Droniq is enabling and testing the connection of the eVTOLs or landing system to its own UAS Traffic Management System (UTM).
To do this, Droniq leverages its products and solutions for drone traffic integration, such as antenna sensing and UTM environment.
With these technologies, Droniq supports the positioning and guidance of eVTOLs and ensures the flow of information between eVTOLs and other air traffic participants within the UTM.

Project partner
AIRBUS
DRONIQ
KASAERO
KYMATI
TU Munich
University Stuttgart
Funding source