Glossary
Definitions, abbreviations from unmanned aviation
-
A
-
B
-
C
-
D
-
E
-
F
-
G
-
H
-
I
-
J
-
K
-
L
-
M
-
N
-
O
-
P
-
Q
-
R
-
S
-
T
-
U
-
V
-
W
-
X
-
Y
-
Z
-
A-NPA - Advance Notice of Proposed AmendmentPreliminary draft European regulations
-
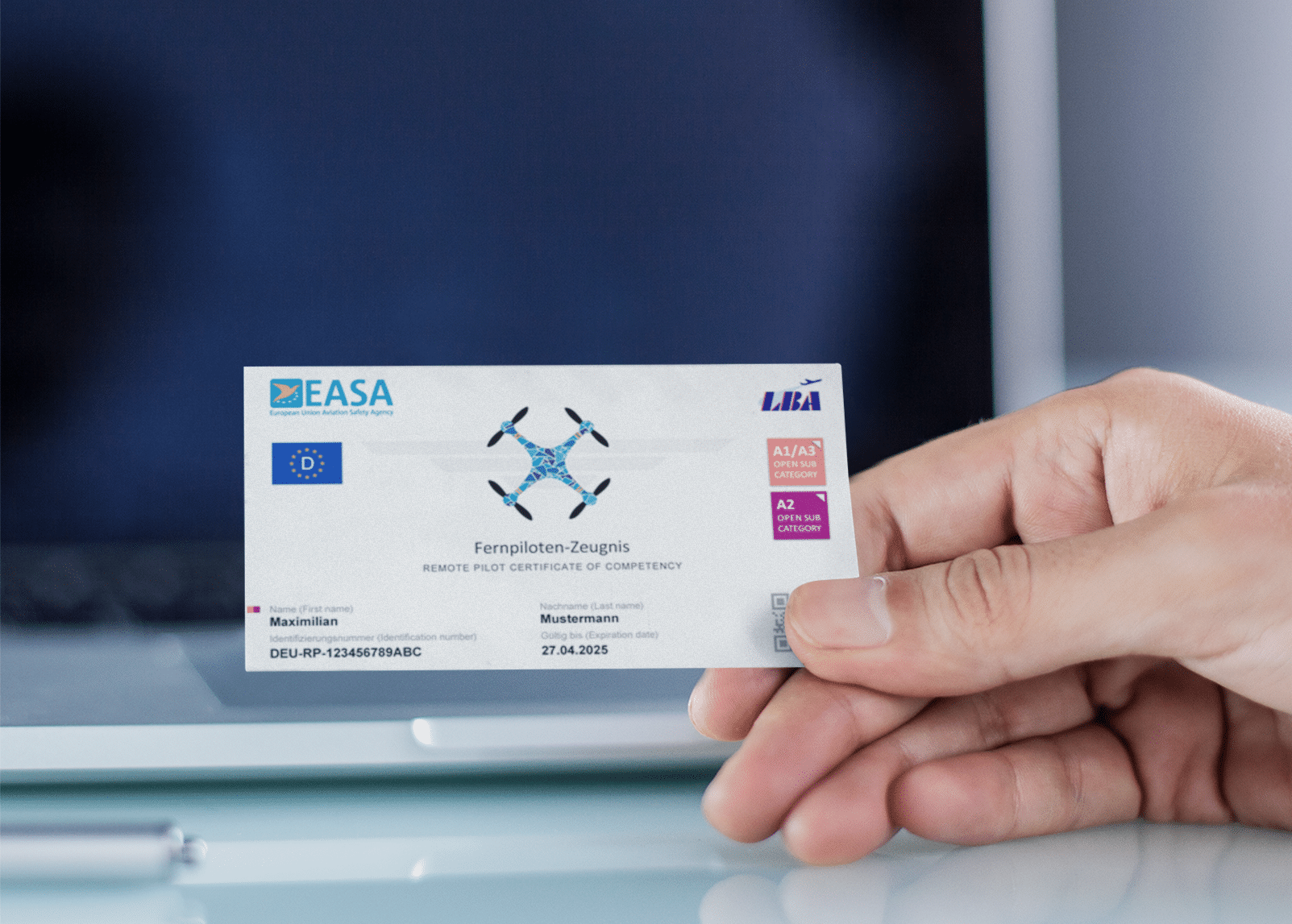
A1/A3 Remote Pilot Certificate
The A1/A3 remote pilot certificate is the first level in the European drone pilot license system. It entitles the holder to pilot drones in categories A1 and A3 (open category) and is mandatory for drones with a take-off weight of over 250 g. The training and examination take place online via the Luftfahrt-Bundesamt (LBA).
-
A2 Remote Pilot Certificate
The A2 remote pilot certificate is required for advanced missions in the open category - for example when flying closer to uninvolved persons. In addition to the A1/A3 certificate, an additional theoretical examination and practical self-declaration are required. It is also processed via the LBA.
-
A2 refresher training / refresher training
The A2 refresher course is designed to refresh the A2 remote pilot certificate. Here, drone pilots refresh their theoretical knowledge of flight rules, safety and airspace so that they can continue to fly drones safely and in accordance with the rules in extended operations.
-
ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast)
A monitoring system for aircraft that transmits position data to ground stations and other aircraft.
-
Aerial Survey
A method of mapping and collecting data from the air, often using drones equipped with cameras and sensors.
-
Aerial Thermography
The use of drones to capture infrared images to identify temperature differences on surfaces.
-
AGL - Above Ground LevelHeight above ground
-
AIP - Aeronautical Information PublicationThe Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP) is a collection of aviation orders, information, and notices that are valid for an extended period of time.
It contains, among other things, a list of all airfields including airfield boundaries and contact details of air traffic control units.
-
AirspaceFrom the perspective of air traffic control, airspace is a three-dimensional space, interwoven with a network of flight paths and divided into different airspace classes, depending on the control services offered.
-
Airspeed
The speed of a drone relative to the surrounding air.
-
Altimeter
A device that measures the altitude of the drone above sea level, often integrated into the altimeter.
-
AltMoc - Alternative Means of ComplianceAlternative detection methods
-
AMC - Acceptable Means of ComplianceAccepted detection methods
-
APAS - Advanced Pilot Assistant System
APAS refers to both obstacle detection and collision avoidance for drones.
-
ARC - Air Risk ClassRisk class air
-
ATF - Almost Ready to Fly
An ATF-style drone no longer requires many setup steps or additional accessories to be put into operation.
-
ATM - Air Traffic ManagementAir Traffic Management (ATM) is the central task of air traffic control. The aim is to organize air traffic in the allocated airspace safely, smoothly and economically.
-
ATTI - Attitude ModeOperating mode with DJI without GPS
-
ATZ - Aerodrome Traffic ZoneAirfield traffic zone
-
Ascent permit
For certain drones in Germany, a take-off permit is required, which must be obtained from the competent authority.
-
Automatic operation
A drone is in automatic mode when it flies a pre-planned route itself, but the remote pilot can still change the route manually.
-
Autonomous operationAn operation in which the unmanned aircraft is in operation without the remote pilot being able to intervene
-
Autopilot
An autopilot takes over the operation of an aircraft automatically. This means that the pilot does not have to steer during this time.
-
AUW - All Up Weight
The AUW describes the take-off weight including all components.
-
Stock drone
A stock drone is a drone that has no classification.
-
Baro
Barometer is a flight mode in which the drone can maintain its altitude independently.
-
BDL - Federal Association of the German Air Transport Industry e. V.The BDL (Bundesverband der Deutschen Luftverkehrswirtschaft e. V.) is an association representing the interests of the German air transport industry.
-
Notified bodyExamination station (PStF) designated by the Luftfahrt-Bundesamt to conduct theory examinations for remote pilots according to UAS.OPEN.030(2)c) in Part A of the Annex to DVO (EU) 2019/947.
-
Unmanned aerial vehicle observerA person who is adjacent to the remote pilot and, through unassisted visual observation of the unmanned aircraft, assists the remote pilot in maintaining the unmanned aircraft in VLOS and safely conducting the flight.
-
Stock drone
A stock drone is a drone that has no classification.
-
Operating description / ConOps operating conceptThe abbreviation ConOps stands for Concept of Operations. A concept of operations contains information on operations and describes procedures for safe UAS operation. The exact scope of the concept of operations depends on the risk category previously determined in the SORA. The ConOps is created by the operator of the UAS.
-
Operating category
Drones are classified into different operating categories depending on various factors. There are 3 categories which are divided as follows: open, special and subject to approval.
-
BFU - Federal Bureau for Aircraft Accident InvestigationNational Civil Aviation Accident and Incident Investigation Center.
-
BLAG-UAS/FM - Federal-State Working Group UAS and Model AircraftThe Federal-Länder Working Group (BLAG) for "Unmanned Aerial Systems and Aeromodels" consists of the Federal Ministry of Transport (BMVI), the respective state aviation authorities (LLB) and DFS Deutsche Flugsicherung GmbH (DFS). Remote pilots can obtain information on the subject of drone flight from a joint website: https://www.dfs.de/dfs_homepage/de/Drohnenflug/Start/
-
BMDV - Federal Ministry of Digital Affairs and TransportSupreme Aviation Authority for Civil Aviation Affairs
-
Ground sensors
The ground sensor system is a system for ground-based air situational awareness.
-
BOS - authorities and organizations with security tasksInstitutions that are entrusted with the defense against hazards fall under the collective term authorities and organizations with security tasks (BOS).
-
BVLOS - Beyond Visual Line of SightThe term stands for "beyond visual line of sight". Refers to drone operation beyond the visual line of sight of the remote pilot. For such operations, private and commercial users need a special permit from the responsible aviation authority. BOS forces are exempt from this requirement. They are exempt from the corresponding requirements in the event of an operation.
-
C classification (CE marking)
New drones require a CE classification (C0-C6) in order to be operated in compliance with the law. The class defines the intended use (e.g. in close proximity to people) for which the drone is suitable. From 2024/25, CE-certified devices will be mandatory for many subsidies and forms of operation.
-
C2 Link ServiceA communication service provided by a third party that ensures command and control between the unmanned aircraft and the control unit (CU).
-
Calibration
The process of aligning and adjusting a drone's sensors to ensure accurate measurements.
-
CE markingA marking by which the manufacturer declares that the product complies with the applicable requirements set out in the Union harmonization legislation under which the affixing of the marking is required.
-
Certified Category - Category subject to approvalA UAS operating category as defined in Article 6 of the Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/947.
-
Cinewhoop
A small, maneuverable drone that is used for indoor flights and FPV videos.
-
CISP (Common Information Service Provider)Provides the USSP with all relevant airspace and air traffic data for the provision of U-Space services.
-
Collision Avoidance System
An advanced system that recognizes obstacles and automatically takes measures to avoid them.
-
ConOps - Concept of OperationsThe abbreviation ConOps stands for Concept of Operations. A concept of operations contains information on operations and describes procedures for safe UAS operation. The exact scope of the concept of operations depends on the risk category previously determined in the SORA. The ConOps is created by the operator of the UAS.
-
Continuous monitoring
The continuous monitoring of certain areas or facilities using drones.
-
CORUS-XUAM
CORUS-XUAM is a two-year demonstration project that aims to show how U-Space services and solutions can support the integrated flight operations of Urban Air Mobility (UAM).
-
CTR (Controlled Traffic Region)
A controlled airspace around airports where special rules and clearances are required for drone operations.
-
D&A - Detect & AvoidDetect & Avoid. A D&A system detects obstacles and avoids them independently.
-
DAeC - German Aero ClubLargest air sports association in Germany.
-
DAT (Detect And Avoid Technology)
Technology that enables drones to recognize and avoid obstacles in order to avoid collisions.
-
Data Link
A communication channel that connects the drone to the ground station and enables the exchange of control commands and telemetry data.
-
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
A 3D model of the earth's surface created by drone mapping that shows the height of the terrain.
-
Direct remote identificationA system that provides for the local transmission of information about an unmanned aerial vehicle in operation, including identification of the unmanned aerial vehicle, so that such information can be retrieved without physical access to the unmanned aerial vehicle.
-
DJI
DJI is a well-known Chinese manufacturer of drones and UAVs.
-
DJI FlyCart 30 Series
The DJI FlyCart 30 is your solution for heavy-duty air freight: up to 30 kg payload in cargo or winch mode, range of 28 km (without load) or 16 km (with load), fully automated, IP54-certified. Included models: DJI FlyCart 30 - up to 30 kg payload, cargo/winch mode, 28 km flight distance without payload, 16 km with full load
-
DJI Go App
A mobile application for controlling and configuring DJI drones.
-
DJI Matrice 30 Series
The Matrice 30 series combines compact portability with industry standards: Integrated wide-angle, zoom and laser rangefinder sensors enable precise inspections with up to 41 min flight time and IP55 protection.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 30 - 48 MP zoom camera (5×-16× optical), 12 MP wide angle, laser rangefinder up to 1,200 m
- DJI Matrice 30T - like M30 plus 640 × 512 px radiometric thermal camera
DJI Matrice 300 & 350 RTK series
Robust RTK platforms for long-term missions: Up to 55 min flight time, dual-battery hot-swap, IP45/55, 15 km transmission and 6-way obstacle detection ensure maximum reliability.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 300 RTK - 55 min flight time, 15 km 1080p transmission, IP45, 6-directional sensing, -20 °C to 50 °C
- DJI Matrice 350 RTK - 55 min flight time, IP55, dual-battery system with hot-swap, O3 Enterprise Transmission, Night-Vision FPV camera
-
DJI Matrice 300/350 RTK series
Robust RTK platforms for long-term missions: Up to 55 min flight time, dual-battery hot-swap, IP45/55, 15 km transmission and 6-way obstacle detection ensure maximum reliability.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 300 RTK - 55 min flight time, 15 km 1080p transmission, IP45, 6-directional sensing, -20 °C to 50 °C
- DJI Matrice 350 RTK - 55 min flight time, IP55, dual-battery system with hot-swap, O3 Enterprise Transmission, Night-Vision FPV camera
-
DJI Matrice 400 Series
The DJI Matrice 400 (M400) series is a modular, high-performance enterprise platform for demanding industrial and public safety missions. It combines robust construction with long flight time, flexible payload integration and extensive sensor support - ideal for inspection, surveying, rescue and more. Included models: DJI Matrice 400
-
DJI Matrice 4D/4TD Series
The Matrice 4D/4TD series is designed for autonomous 24/7 use with DJI Dock 3. IP55-certified, anti-ice propellers, LiDAR-based obstacle detection and up to 47 minutes of flight time ensure maximum data output with minimum maintenance.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 4D - Standard version with 4K wide-angle and telephoto camera, anti-ice propeller blades
- DJI Matrice 4TD - like 4D plus 640 × 512 px infrared thermal camera for night and thermal imaging missions
-
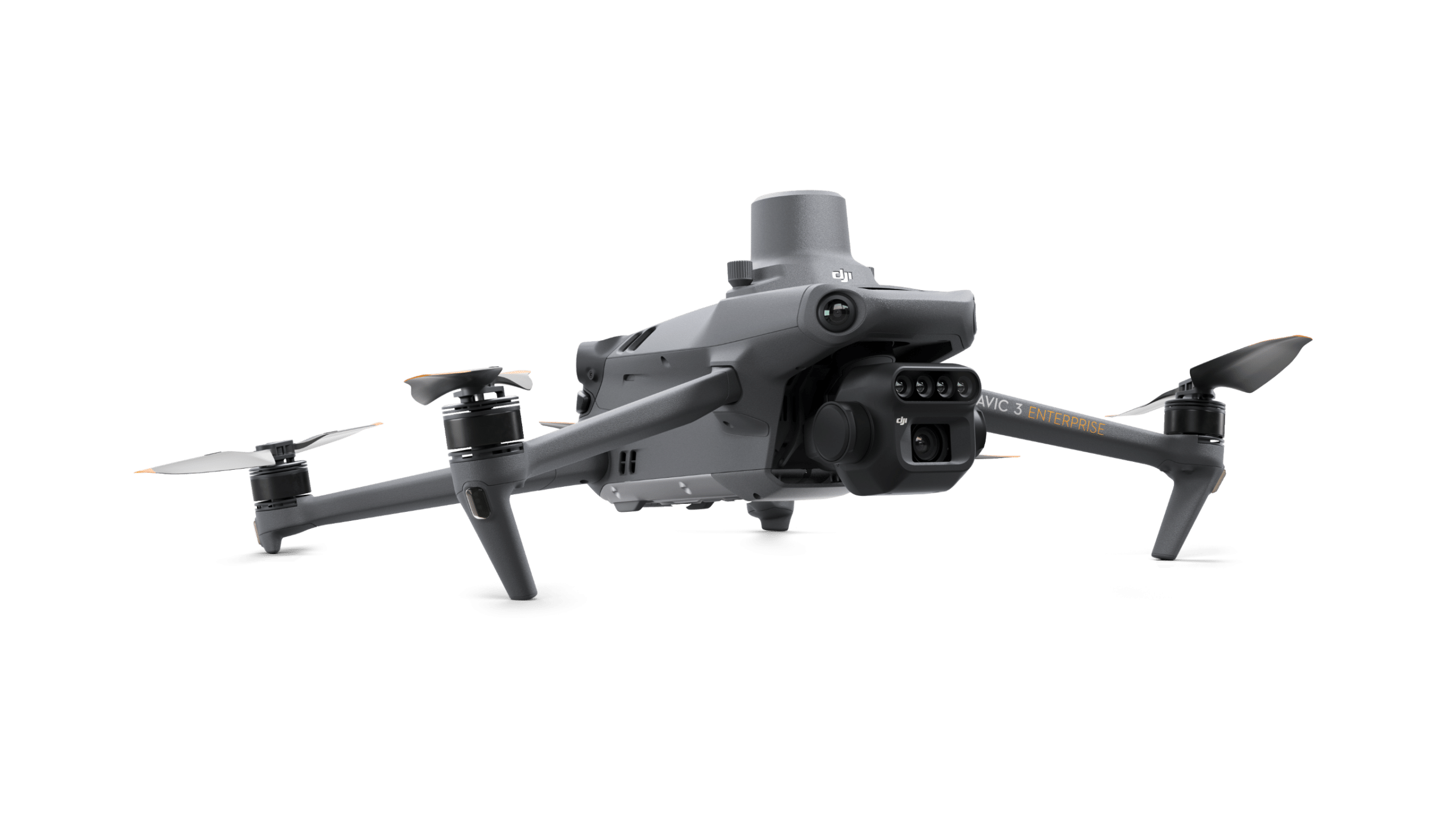
DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise Series
The DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise series defines new standards for compact professional drones and combines high-resolution imaging with RTK precision in a foldable housing. Thanks to the mechanical shutter and 56× hybrid zoom, every mission - from surveying to inspection - is particularly efficient. The series includes the following models: DJI Mavic 3E with 4/3″ CMOS and mechanical shutter, the DJI Mavic 3T with additional 48 MP telephoto camera and radiometric thermal camera as well as the DJI Mavic 3M with a multispectral camera for agricultural analysis and RTK as standard.
-
Draw Mode
With the drawing mode, you can draw a route on the screen yourself and the drone will then take over this route.
-
Drones
Drones are unmanned aerial vehicles that can be remote-controlled or program-controlled directly by humans.
-
Drone liability insurance
Drone liability insurance covers damage caused to third parties by the operation of a drone. It is required by law in Germany and protects drone pilots against high financial risks.
-
Fully comprehensive drone / hull insurance
Comprehensive drone insurance adds personal protection to liability insurance. It covers costs in the event of a crash, operating errors or technical defects and offers pilots maximum security when using drones professionally.
-
Drone operators
An operator of a drone.
-
Drone detection
Drone detection refers to the detection and tracking of drones in airspace. It is essential for safety-critical areas such as airports, power plants or major events. Modern systems work with RF detection, radar, camera or acoustic sensors. Droniq offers the Senhive SenID+ system, among others.
-
Drone detection
Drone detection refers to the use of sensors and software to identify drones in airspace. It is used for security at major events, perimeter protection and to protect critical infrastructure, among other things.
-
Drone driver's license
It is a certificate that you obtain as part of a training course and examination and shows that you are capable of operating a drone safely.
-
Drone Garage
See Drone-in-a-Box System
-
Drone liability insurance
Drone liability insurance protects you if you cause damage with your drone and have to bear the financial consequences.
-
Drone hangar
See Drone-in-a-Box System
-
Drone pilot
A drone pilot is someone who controls unmanned aerial vehicles.
-
Drone radar
A drone radar is a technical system for monitoring airspace. It detects, tracks and visualizes drone movements in real time - important for flight safety, drone detection and the protection of sensitive areas.
-
Drone registration
Drone registration is a legal requirement in the EU. Every drone operator must label their drone with a unique registration number (eID) to ensure traceability and safety in air traffic.
-
Drone sighting
A drone sighting is the visual perception or technical detection of a drone. This information is relevant for authorities, security services and organizations to assess potential dangers.
-
Drone sighting
Drone sighting is the visual perception or technical detection of a drone. It is important for security authorities, emergency services and operators in order to identify potential risks in the airspace at an early stage
-
Drone Regulation
The Drone Ordinance contains all the regulations for drones that apply in Germany.
-
Drone insurance
Drone insurance is a combination of liability and optional hull cover. It is indispensable for private and commercial drone pilots and ensures legal security and risk minimization.
-
Drone-in-a-Box system (DIB)
A drone-in-a-box (DIB) system or drone garage / drone hangar is a highly automated drone system. It is used to perform autonomous drone flights beyond the pilot's line of sight (BVLOS). The drone is controlled via a control station. A pilot on site is no longer necessary. Since the drone is located in and protected by a box, missions can take place at any time and in almost any weather.
-
Drones-as-a-Service (DaaS)
Drones as a Service (DaaS) is a concept in which drones and the associated infrastructure are offered as a service. Instead of owning and operating drones themselves, companies or individuals can use the services of specialized providers.
As part of DaaS, providers typically take on various tasks, including providing the drones, training operators, conducting flights, analyzing data and reporting. Customers can access a variety of services depending on their needs, including aerial photography, inspections, monitoring, mapping and much more.
This model offers companies the advantage of using drone technology without the associated costs and complexities. It also allows for flexible scaling depending on the requirements of a particular project or task. DaaS has the potential to improve efficiency and safety in various industries and open up new fields of application for drone technology.
-
Dual-band GPS
A GPS system that uses both the L1 and L2 frequency bands to enable more accurate positioning.
-
DWD - German Weather ServiceThe DWD is a federal agency based in Offenbach am Main. Its main task is to monitor the climate in Germany and to warn of weather-related hazards. By providing basic weather information, the German Weather Service supports UAS of both meteorological flight preparation. The information includes ground wind forecasts as well as precipitation radar and lightning maps. For commercial drone operators, the DWD also offers a fee-based self-briefing system.
-
Dynamic Home Point
A function that updates the starting point of the drone during the flight based on the position of the controller.
-
Drone detection
Drone detection refers to the use of sensors and software to identify drones in airspace. It is used for security at major events, perimeter protection and to protect critical infrastructure, among other things.
-
EASA - European Aviation Safety AgencyEuropean Aviation Safety Agency is the aviation safety authority of the European Union. It was established on July 15, 2002, by decision of the European Council and has been based in Cologne since November 2004. Operations began on September 28, 2003, and it has been fully operational since 2006. EASA currently has about 400 employees.
-
ED-D
ED-D means danger area and describes an area that harbors dangers for missiles.
-
ED-RThe abbreviation ED-R stands for restricted area. This refers to a defined airspace above the territory of a state in which aircraft flights are subject to temporary or permanent restrictions. Examples are airspaces over nuclear power plants or over the Berlin government district. Corresponding areas are defined to prevent threats to public safety and order. Whether a UAS is allowed to fly into an ED-R depends on the restriction. An unauthorized entry is a criminal offense.
-
EIS (Electronic Image Stabilization)
A technology that digitally compensates for camera shake in videos to ensure smoother recordings.
-
EO/IR sensor
An electro-optical/infrared sensor used to capture visible and infrared images, often for surveillance and rescue missions.
-
ESC (Electronic Speed Controller)
A component that controls the motor of a drone and regulates the speed of the propellers.
-
EVLOS (Extended Visual Line of Sight)Operation in extended visibility: Either airspace observers provide an airspace observation or take over the control and are from now on new remote pilots.
-
DJI FlyCart 30 Series
The DJI FlyCart 30 is your solution for heavy-duty air freight: up to 30 kg payload in cargo or winch mode, range of 28 km (without load) or 16 km (with load), fully automated, IP54-certified. Included models: DJI FlyCart 30 - up to 30 kg payload, cargo/winch mode, 28 km flight distance without payload, 16 km with full load
-
Fail safe mode
The drone flies back to the starting point using the GPS data if it loses the connection to the controller.
-
Feet (feet, ft)English measure of length used in aviation to designate flight altitude. One foot is equal to 30.48 cm.
-
Remote pilotA natural person who is responsible for the safe conduct of the flight of an unmanned aircraft, where the remote pilot:in either provides flight control manually or, if the unmanned aircraft is flying automatically, monitors its course and remains able to intervene and change course at any time.
-
Remote pilot certificate A1/A3
The A1/A3 remote pilot certificate is the first level in the European drone pilot license system. It entitles the holder to pilot drones in categories A1 and A3 (open category) and is mandatory for drones with a take-off weight of over 250 g. The training and examination take place online via the Luftfahrt-Bundesamt (LBA).
-
Remote pilot certificate A2
The A2 remote pilot certificate is required for advanced missions in the open category - for example when flying closer to uninvolved persons. In addition to the A1/A3 certificate, an additional theoretical examination and practical self-declaration are required. It is also processed via the LBA.
-
Remote Pilot Certificate STS (Standard Scenario)
The STS certificate is required for flights in the "special category" according to a standard scenario (e.g. STS-01: BVLOS flight in visual range over a controlled area). It replaces the former national "large EU remote pilot certificate" and requires practical training and an examination at a recognized test centre.
-
Remote control
As the term itself suggests, you control the drone from a distance, i.e. the drone does not need to be connected to a cable.
-
FLARMTraffic information and collision avoidance system for general aviation, light aircraft and drones.
-
Flight Controller
The central control unit of a drone that controls stability and navigation in flight.
-
FLIR
FLIR (Forward Looking Infrared) stands for thermal imaging cameras that are used on drones. They enable the thermal detection of people, buildings or facilities and are used in areas such as rescue operations, inspections or agriculture.
-
Restricted flight area
A restricted flight area is an airspace of defined dimensions in which aircraft flights are restricted due to certain conditions. The restrictions can be permanent or temporary.
-
Flight logIn the flight logbook, the remote pilot documents his drone flights (electronically or in paper form). Among other things, it contains information about the date and time of the flight, the name of the remote pilot, the total duration of the mission on site, and the number of takeoffs and landings. The documentation is not mandatory in Germany. However, as part of an ascent permit or other exemption from operating bans, the operator of a drone may be required to keep a flight log in the ancillary provisions.
-
Flight modelNational: Unmanned aircraft, including their control station, operated exclusively for sport and recreational purposes.
-
Model aircraft club or associationAn organization legally established in a Member State for the purpose of conducting recreational flights, air shows, sporting activities or competitions with UAS.
-
Flight radar
An airborne radar displays the position and movements of aircraft in real time. In addition to traditional aviation, flight radar is also becoming increasingly important for drone operations and airspace surveillance.
-
Air cab
An air cab is an aircraft that is used to transport passengers or freight inland.
-
No-fly zone / Geographical areas
No-fly zones or geographical areas are defined areas in which drone flights are restricted or prohibited. These include airports, crowds of people or critical infrastructure. Violations can have legal consequences.
-
FlyawayUncontrolled drifting or flying away of a drone
-
Follow-me modeA mode of operation of a UAS in which the unmanned aircraft continuously follows the remote pilot within a predetermined radius.
-
FPV (First Person View)
A mode in which the pilot controls the drone from a first-person perspective, usually using a camera on the drone and a connected display or goggles.
-
FPV Goggles
Goggles that provide the pilot with a live view from the drone's camera.
-
Friend or foe recognition
Friend or foe detection is used to distinguish your own drones from potentially dangerous or unknown aircraft. It is a central component of modern drone security systems.
-
No-fly zone / Geographical areas
No-fly zones or geographical areas are defined areas in which drone flights are restricted or prohibited. These include airports, crowds of people or critical infrastructure. Violations can have legal consequences.
-
GBSAS - Ground-Based Situational Awareness System
The mobile traffic receiving station (Ground-Based Situational Awareness System, GBSAS) is used to support UAS operations and provides the user with an air situation picture in the area around the deployment site. The mobile station receives FLARM® and ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance - Broadcast) signals transmitted by gliders, helicopters, motorized aircraft or other air traffic participants in the airspace.
-
Dangerous goodsArticles or substances carried by an unmanned aerial vehicle as a payload that pose a risk to health, safety, property or the environment in the event of an incident or accident, in particular: - explosive substances (danger of mass explosion, danger from splinters, explosive and thrown pieces, low danger from air blast, high danger of fire, explosives, extremely insensitive explosives),- gases (flammable gases, non-flammable gases,toxic gases, oxygen, danger when inhaled),- flammable liquid substances (flammable liquid substances, flammable substances, fuel oil, gasoline),- flammable solids (flammable solids, spontaneously combustible solids, dangerous in contact with water),- oxidizing substances and organic peroxides,- toxic and infectious substances (poison, biohazard),- radioactive substances,- corrosive substances
-
Geo-awareness Service ProviderThe Geo-awareness Service is governed by Regulation (EU) 2019/945. It refers to UAS capabilities and the requirements for Member States when they decide to establish geographic zones or for UAS operators to follow and comply with the specification of these zones. This service is intended to assist UAS operators in meeting these obligations, as it will provide this information (where they may and may not fly) with appropriate accuracy. By using this service in a U-Space airspace, UAS operators can fulfill their responsibilities related to this UAS operator obligation.
-
Geo-fencing
A technology that draws virtual barriers around certain areas to restrict the drone's flight to these areas.
-
Geo-sensitizationA function that, based on data provided by Member States, detects a potential airspace boundary violation and alerts remote pilots so that they can take immediate and effective action to prevent it.
-
Geo zones
Geo zones are geographically defined airspace areas in which certain drone flight rules apply. They can include no-fly zones, altitude restrictions or special permits. Compliance with geo-zones is mandatory and is often visualized digitally via flight apps.
-
Geographical UAS areaA portion of airspace defined by the competent authority that allows, restricts, or excludes UAS operations to address the safety, privacy, and personal data, security, or environmental risks associated with UAS operations.
-
GimbalCardanic suspension, Multi-axis stabilization device for the camera
-
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)
A collective term for satellite navigation systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou.
-
GPS (Global Position System)US Global Satellite System
-
GRC (Ground Risk Class)Soil risk class.
-
Drone liability insurance
Drone liability insurance covers damage caused to third parties by the operation of a drone. It is required by law in Germany and protects drone pilots against high financial risks.
-
HALE (High Altitude Long Endurance)Great height, long reach.
-
Headless mode
A mode in which the drone control is independent of the orientation of the drone.
-
High-Altitude Platform Station (HAPS)
An unmanned platform that flies at high altitude and is used for communication or surveillance purposes.
-
High-Resolution Imaging
Capturing images with a high level of detail using special cameras on drones.
-
HoD - Hook-on-Device
The Hook-on-Device (HOD) is a device for transmitting your own position data for UAS.
-
Hovering
The hovering of a drone in the air at a fixed position without noticeable movement.
-
ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization)International Civil Aviation Organization.
-
IFR (Instrument Flight Rules)Instrument flight rules
-
IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit)
A sensor that measures the drone's movements and helps to stabilize its position and orientation.
-
Inertial Navigation System (INS)
A navigation system that measures acceleration and rotational movements to determine the position of the drone.
-
Inspection Drone
A drone specially equipped for inspection tasks such as bridge, wind turbine and pipeline inspections.
-
Intelligent Flight Modes
Predefined flight modes that enable complex maneuvers and automatic functions, such as "Follow Me" or "Waypoint Navigation"
-
J (Joule)Unit of measurement for energy
-
JARUS (Joint Authorities for Rulemaking on Unmanned Systems)International Working Group on Drone Regulation.
-
K-index
A measure of geomagnetic activity that can influence the conditions for GPS reception.
-
Proof of knowledge
A certificate of proficiency shows whether you have knowledge of the basics of using and navigating model aircraft. It also shows that you are aware of the legal basis and the local airspace regulations. This proof of knowledge is required if you wish to operate a drone with a take-off mass of at least 2 kg.
-
Labeling obligation
The labeling requirement states that drones weighing at least 250g must be labeled with the owner's name and address.
-
kmz /kml (Keyhole Markup Language)A file that can be loaded as a layer in e.g. Google Earth. The kmz is a compressed version of the kml.
-
Controlled area on the groundAn area on the ground within which the UAS is operated and the UAS operator can ensure that only involved persons are present.
-
Cooperative drones
Cooperative drones are equipped with transponders or remote ID systems that actively transmit their position to ground stations or other aircraft. They increase transparency and safety in the airspace.
-
LBA - German Federal Aviation AuthorityThe Federal Office of Civil Aeronautics, headquartered in Braunschweig, is the higher federal authority for all civil aviation tasks in Germany. The LBA is subject to the technical and official supervision of the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure.
-
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
A distance measurement technology that uses laser light to create precise 3D maps and models of the environment.
-
Lithium-Polymer (LiPo) Battery
A widely used battery technology for drones, known for its high energy density and performance.
-
LOS (Line Of Sight)
Flights where the pilot can see the drone visually at all times.
-
LUC (light UAS operator certificate) - operator certificate for light UASLight UAS Operator Certificate (LUC) is a certificate for a UAS operation issued by the responsible aviation authority. Operators can self-assess the risk of operation in the special category.
-
PilotSee remote pilot
-
AirspaceFrom the perspective of air traffic control, airspace is a three-dimensional space, interwoven with a network of flight paths and divided into different airspace classes, depending on the control services offered.
-
Airspace golfAirspace G (pronounced Luftraum Golf) is the lowest airspace in Germany.Its lower boundary begins on the ground and its upper boundary, in line with Airspace E above it, is usually 2,500 feet, or 762 meters. Airspace G is the only uncontrolled airspace in Germany. The ascent of a drone does not require air traffic control clearance by, for example, DFS. However, the use can be further restricted by other laws and regulations, e.g. regarding nature conservation.
-
Airspace ObserverA person who assists the remote pilot by scanning the airspace in which the unmanned aircraft is operating for potential airborne hazards through unassisted visual scanning.
-
DJI Matrice 30 Series
The Matrice 30 series combines compact portability with industry standards: Integrated wide-angle, zoom and laser rangefinder sensors enable precise inspections with up to 41 min flight time and IP55 protection.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 30 - 48 MP zoom camera (5×-16× optical), 12 MP wide angle, laser rangefinder up to 1,200 m
- DJI Matrice 30T - like M30 plus 640 × 512 px radiometric thermal camera
DJI Matrice 300 & 350 RTK series
Robust RTK platforms for long-term missions: Up to 55 min flight time, dual-battery hot-swap, IP45/55, 15 km transmission and 6-way obstacle detection ensure maximum reliability.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 300 RTK - 55 min flight time, 15 km 1080p transmission, IP45, 6-directional sensing, -20 °C to 50 °C
- DJI Matrice 350 RTK - 55 min flight time, IP55, dual-battery system with hot-swap, O3 Enterprise Transmission, Night-Vision FPV camera
-
DJI Matrice 300/350 RTK series
Robust RTK platforms for long-term missions: Up to 55 min flight time, dual-battery hot-swap, IP45/55, 15 km transmission and 6-way obstacle detection ensure maximum reliability.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 300 RTK - 55 min flight time, 15 km 1080p transmission, IP45, 6-directional sensing, -20 °C to 50 °C
- DJI Matrice 350 RTK - 55 min flight time, IP55, dual-battery system with hot-swap, O3 Enterprise Transmission, Night-Vision FPV camera
-
DJI Matrice 400 Series
The DJI Matrice 400 (M400) series is a modular, high-performance enterprise platform for demanding industrial and public safety missions. It combines robust construction with long flight time, flexible payload integration and extensive sensor support - ideal for inspection, surveying, rescue and more. Included models: DJI Matrice 400
-
DJI Matrice 4D/4TD Series
The Matrice 4D/4TD series is designed for autonomous 24/7 use with DJI Dock 3. IP55-certified, anti-ice propellers, LiDAR-based obstacle detection and up to 47 minutes of flight time ensure maximum data output with minimum maintenance.
Included models:
- DJI Matrice 4D - Standard version with 4K wide-angle and telephoto camera, anti-ice propeller blades
- DJI Matrice 4TD - like 4D plus 640 × 512 px infrared thermal camera for night and thermal imaging missions
-
DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise Series
The DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise series defines new standards for compact professional drones and combines high-resolution imaging with RTK precision in a foldable housing. Thanks to the mechanical shutter and 56× hybrid zoom, every mission - from surveying to inspection - is particularly efficient. The series includes the following models: DJI Mavic 3E with 4/3″ CMOS and mechanical shutter, the DJI Mavic 3T with additional 48 MP telephoto camera and radiometric thermal camera as well as the DJI Mavic 3M with a multispectral camera for agricultural analysis and RTK as standard.
-
Magnetometer
A sensor that measures the earth's magnetic field and is used to determine the direction.
-
MALE (Medium Altitude Long Endurance)Medium height, long range.
-
Mandatory ServicesIn order to be able to establish a U-Space, EASA has defined so-called "Mandatory Services". These are mandatory services that determine the design of the U-Space: - Network Identification Service - Geo-awareness Service - UAS Flight Authorization Service - Traffic Information Service.
-
Mapping Drone
A drone specially developed for creating maps and 3D models.
-
Mapping software
Special software for processing and analyzing drone images to create maps and 3D models.
-
CrowdsA multitude of people standing so close together that it is almost impossible for a single person to move away from this crowd.
-
MHz (Megahertz;)Unit of measurement for radio frequency.
-
Microdrone
A very small drone, often weighing less than 250 grams, used for indoor or special applications.
-
Model airplaneAn unmanned aerial vehicle system used primarily for recreational activities.
-
MSL (Mean Sea Level)(Height above) sea level.
-
MTOM (maximum take-off mass) - Maximum permissible take-off massThe maximum allowable mass of the unmanned aircraft, including payload and fuel, as determined by the manufacturer or builder, with which the unmanned aircraft can be operated. Synonyms: MTOW, Maximum Takeoff Mass, Maximum Takeoff Weight.
-
Multicopter
Multicopter describes flying objects with more than one propeller or rotors on one plane.
-
N/A (Not Applicable)Not available.
-
NightThe hours between the end of civil twilight and the beginning of civil dawn as defined in the Executive Order.
-
night vision cameraA night vision camera provides clear images in the dark – ideal for rescue, security, inspection, and agriculture. Different technologies are used depending on the model: 1) Thermal imaging camera: Detects temperature differences, 2) Starlight/low-light sensor: Amplifies existing light, 3) NIR spotlight: Illuminates scenes with invisible infrared light. DJI offers various drones with night vision cameras, such as the Mavic 4 Thermal, Matrice 400 with H30T or H30N – perfect for night-time operations.
-
Nadir
The point directly under the drone, often used for mapping and photography.
-
NDB (Non-Directional Beacon)Undirected beacon. Position determination in manned air navigation.
-
Network Identification ServiceThe Network Identification Service ensures traceability of the unmanned aircraft during its flight. Based on this information, USSPs can actually exchange UAS traffic information with each other, providing traffic information for UAS operations.
-
No-Fly Zone
An area where drone flights are prohibited, often for safety or data protection reasons.
-
NOTAM (Notice To Airmen)Information on temporary and permanent changes to the Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP).
-
PayloadSee Payload.
-
Obstacle Avoidance System
A technology that detects obstacles in the drone's flight path and automatically avoids them.
-
Obstacle Detection
A system for detecting and avoiding obstacles during flight, often using ultrasonic, infrared or laser sensors.
-
Open Category - Open CategoryA UAS operating category as defined in Article 4 of the Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/947.
-
Operator
The drone pilot is often referred to as the operator.
-
Orthomosaic
A highly accurate, rectified aerial image, which consists of many individual photos and serves as georeferenced map material.
-
P4RTK
A drone model from DJI, known for its precise RTK-GNSS positioning systems.
-
Payload
Instruments, mechanisms, equipment, parts, appliances, accessories, or attachments, including communications equipment, installed in or attached to the aircraft and not used or intended to be used to operate or control the aircraft in flight, but not forming part of the airframe, an engine, or a propeller. Synonym: Payload
-
Payload Release Mechanism
A system that enables the drone to drop cargo or other payloads.
-
Photogrammetry
The science of creating maps and 3D models by analyzing photographs, often through drone imagery.
-
PIC (Pilot in Command)
The pilot who is currently in control of the aircraft.
-
PIS (Public Interest Site)Landing site (of public interest) for helicopters at hospitals.
-
Privately manufactured UASA UAS assembled or manufactured by the builder for his own use, except for UAS assembled from components marketed as a prefabricated kit.
-
PStF - Testing stationSee notified body.
-
Quadcopter
A drone with four propellers that is controlled by different rotation speeds.
-
Drone radar
A drone radar is a technical system for monitoring airspace. It detects, tracks and visualizes drone movements in real time - important for flight safety, drone detection and the protection of sensitive areas.
-
Drone registration
Drone registration is a legal requirement in the EU. Every drone operator must label their drone with a unique registration number (eID) to ensure traceability and safety in air traffic.
-
Flight radar
An airborne radar displays the position and movements of aircraft in real time. In addition to traditional aviation, flight radar is also becoming increasingly important for drone operations and airspace surveillance.
-
RC (Remote Control)Remote control
-
Redundancy
Multiple design of critical systems (e.g. control system, power supply) to ensure reliability.
-
RedundancyA failure of one motor can be compensated by a number of other motors.
-
Remote ID
The Remote ID can be used to identify drones and their operators.
-
Return to Home (RTH)
A safety feature that automatically flies the drone back to the starting point if the signal is lost or the battery runs low.
-
Risk analysis / risk assessment (SORA)A SORA (Specific Operations Risk Assessment) is a method for risk assessment / risk analysis that has been specially developed for the operation of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS). This method is required by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and provides a systematic approach to assessing and minimizing the risks associated with the use of drones.
-
RMZ (Radio Mandatory Zone)Area with radio communication obligation.
-
RobustnessThe effect of the risk mitigation measures, based on the gain in security from those measures and the level of assurance and integrity achieved from the gain in security.
-
Roll
Roll describes the control axis of a drone, which allows the drone to tilt to the left and right.
-
Rotor
A rotor is a part of a machine that turns or rotates.
-
RPIC (Remote Pilot in Command)
Remote pilot who holds a remote control in their hand and flies the drone remotely.
-
RTH (Return To Home)Return to start point (home point); the device returns autonomously to the start point.
-
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic)
A high-precision satellite-based navigation system that uses correction signals to achieve accuracy in the centimeter range and is often used for surveying and mapping tasks.
-
A2 refresher training / refresher training
The A2 refresher course is designed to refresh the A2 remote pilot certificate. Here, drone pilots refresh their theoretical knowledge of flight rules, safety and airspace so that they can continue to fly drones safely and in accordance with the rules in extended operations.
-
Drone sighting
Drone sighting is the visual perception or technical detection of a drone. It is important for security authorities, emergency services and operators in order to identify potential risks in the airspace at an early stage
-
Drone sighting
A drone sighting is the visual perception or technical detection of a drone. This information is relevant for authorities, security services and organizations to assess potential dangers.
-
SAIL (Specific Assurance Integrity Level)Risk level according to SORA to determine countermeasures.
-
SAR (Search And Rescue)Search and Rescue.
-
HoverRemain in the air in a geographical position.
-
Sense and Avoid
An advanced obstacle detection and avoidance system that combines data from various sensors to perform safe maneuvers.
-
SenseFly
A manufacturer of professional drones for surveying and mapping.
-
SERA (Standardised European Rules of the Air)Standardized European Rules of the Air.
-
Signal Loss
This is referred to as a loss of radio communication, for example due to loss of control.
-
Single Common Information Service Provider (SCISP)The Single Common Information Service Provider (SCISP) performs a central role of U-Space. It provides the USSP with all relevant airspace and air traffic data for the provision of U-Space services. In addition, with manned aviation data, all air traffic, manned and unmanned, can be displayed in a combined air situation picture. This is an essential prerequisite for flights beyond the visual range of pilots - and thus for the efficient use of drones.
-
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
A technology that enables drones to determine their position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings
-
Smart Return Home
An advanced function in which the drone returns safely to the starting point, taking into account the current flight conditions.
-
SMH (minimum safety height)Minimum flight altitude for manned air traffic.
-
SOP (Standard Operating Procedures)Standard operating procedure
-
SORA (Specific Operational Risk Assessment)A SORA (Specific Operations Risk Assessment) is a method for risk assessment / risk analysis that has been specially developed for the operation of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS). This method is required by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and provides a systematic approach to assessing and minimizing the risks associated with the use of drones.
-
SORA-GER (Specific Operational Risk Assessment Germany)Risk assessment (German version)
-
Specific Category
A UAS operating category in accordance with Article 5 of Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/947. This includes drone operations with increased risk - such as beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) or in the vicinity of crowds. Operation requires an operating permit from the national aviation authority or the use of an approved standard scenario (STS).
-
Standard scenarioA UAS mode of operation in the "special" category for which a detailed list of risk mitigation measures has been defined and for the application of which, when conducting this mode of operation, the operator can make a declaration to the competent authority.
-
Control unitThe equipment or equipment system for remote control of unmanned aircraft as defined in Article 3(32) of Regulation (EU)2018/1139 that supports control or surveillance of the unmanned aircraft in any phase of flight, excluding infrastructures supporting the control and command link service (C2).
-
ControllerSee remote pilot
-
STS Remote Pilot Certificate (Standard Scenario)
The STS certificate is required for flights in the "special category" according to a standard scenario (e.g. STS-01: BVLOS flight in visual range over a controlled area). It replaces the former national "large EU remote pilot certificate" and requires practical training and an examination at a recognized test centre.
-
Swarm Technology
The coordination of several drones that act together as a unit and complete tasks more efficiently.
-
TapFly
With this mode, you can tap anywhere on the screen and the drone will fly there automatically.
-
Telemetry
The transmission of data on the status and position of the drone in real time to the pilot, including altitude, speed and battery level.
-
Telemetry Link
A communication channel that transmits real-time data such as position, altitude, speed and status of the drone.
-
Terrain Following
A mode in which the drone automatically adjusts its altitude to the terrain to ensure a constant overflight altitude.
-
TetheredTethered(s), wired, tethered drone
-
Thrust-to-weight ratio
The ratio of thrust to the total mass of the drone, a measure of performance.
-
THW (Federal Agency for Technical Relief)Authority in the portfolio of the Federal Ministry of the Interior.
-
Tilt Wing/Tilt RotorTilt-wing aircraft. The drives / wings can be tilted.
-
TMZ (Transponder Mandatory Zone)Zone with transponder obligation.
-
TRA (Temporary Reserved Airspace)Temporarily reserved airspace.
-
Traffic Information ServiceThis service provides the UAS operator with the alerts, flight situation, and known/predicted traffic (e.g., if a tracking service is available). The main objective of the Traffic Information Service is to alert the UAS operator and help to avoid a collision.
-
TransponderThe transponder is used to identify an aircraft. Inquiry pulses transmitted by the secondary radar activate the on-board transponder, which transmits the identity code. This enables perfect identification of the aircraft on the radar screen.
-
U-SpaceA U-Space is an airspace element for the use of unmanned aerial vehicles. The U-Space airspace is clearly demarcated from the rest of the airspace, both in terms of its maximum altitude and its geographical extent. In the U-Space, there are clear organizational structures and processes that manage the individual drone flights (e.g., the registration and deregistration of individual flights, the planning of flight routes, etc.) and at the same time ensure that these take place safely. In addition, these ensure safe and smooth interaction with manned air traffic.
-
U-Space Service Provider (USSP)The U-Space Service Provider coordinates unmanned air traffic in U-Space and is responsible for its safety. To this end, it must provide four different technical services:- Provision of a complete air situation picture for the drone pilots (Traffic Information Service)- Continuous monitoring of drone flight movements in the respective U-Space area (Network Identification Service)- Continuous transmission of relevant airspace information to the drone pilots (Geo-awareness Service)- Provision of services for flight registration and flight authorization for drone pilots (Flight Authorization Service).
-
UA (unmanned aircraft) - Unmanned aircraftAn aircraft that is operated or designed to be operated autonomously or remotely without a pilot on board.
-
UAM (Urban Air Mobility)
UAM refers to the transportation of people by air cab, for example.
-
UAS (unmanned aircraft system) - Unmanned aircraft systemAn unmanned aerial vehicle and the equipment for its remote control. Synonyms: UAV, unmanned aerial system, unmanned aerial vehicle, model aircraft.
-
UAS Flight Authorization ServiceThe goal of this service is to provide USSPs with situational awareness of all UAS traffic to be operated in U-Space, even in uncontrolled airspace. This allows USSPs to apply prioritization rules before authorization is granted. With the information about the intended flight and other information about the type of operation and its duration, as well as some associated aircraft performance, USSPs should be able to manage traffic flow and mitigate potentially conflicting flights before those flights occur. To do this, all USSPs are required to share flight authorization applications with each other when more than one USSP provides U-Space services in U-Space airspace (while, of course, complying with the GDPR requirements).
-
UAS Operator ID
Once the drone pilot has registered, they receive their own operator ID. All drones that you own are marked with this number.
-
UAS operatorsUnmanned Aircraft System Operator. A legal or natural person that operates or intends to operate one or more UAS.
-
Unmanned gliderAn unmanned aircraft that is kept aloft by the dynamic response of the air on the fixed lifting surfaces, not depending on an engine for gliding flight. It may be equipped with an engine for emergency use.
-
Uninvolved personsPersons who are not involved in UAS operation or who are not familiar with the UAS operator's instructions and safety procedures.
-
Uncontrolled airspaceAirspace outside the area of responsibility of air traffic control.
-
Uncooperative drone
Uncooperative drones do not send active signals and are therefore more difficult to detect. Special drone detection systems such as radar, acoustic sensors or cameras are used to identify them.
-
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)
Another word for drone, often used in a military or professional context.
-
UTM (UAS Traffic Management System) - traffic management system for unmanned aircraft systemsThe UAS Traffic Management System (UTM) is a drone traffic management system that provides a combined air situation picture of manned and unmanned aircraft, as well as other functions for safe and efficient drone beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) operations in compliance with regulations. For all phases of flight (pre-flight, in-flight and post-flight phase), the UTM provides authoritative services for the safe operation of UAS in the airspace. In the pre-flight phase, the controller can register in the UTM, plan his mission and cross-check it (Are no-fly zones / airspace restrictions present? Are there other registered flight movements? Do I need an ascent permit or a SORA?). In the in-flight phase, the remote pilot can track his drone in real time and observe other aircraft in a combined aerial situation display, including those outside the user's line of sight (manned as well as unmanned registered in the UTM). He also receives real-time data such as photos or videos as needed. The UTM components of the post-flight phase help with the evaluation and follow-up of the flight (e.g., maintenance of the logbook, incident management, battery management).
-
UVC (Ultra-Violet Camera)
A camera that captures UV light and is used to inspect materials and surfaces to detect damage or wear.
-
Fully comprehensive drone / hull insurance
Comprehensive drone insurance adds personal protection to liability insurance. It covers costs in the event of a crash, operating errors or technical defects and offers pilots maximum security when using drones professionally.
-
Drone insurance
Drone insurance is a combination of liability and optional hull cover. It is indispensable for private and commercial drone pilots and ensures legal security and risk minimization.
-
VFR (Visual Flight Rules)VFR flights are "see and be seen" flights where the pilot orients himself to external reference points (lakes, railroad lines, highways, etc.). VFR flights are not under the control of air traffic control or a controller; pilots are responsible for avoiding collisions with other airspace users.
-
Visual Observer
A person who monitors the airspace and supports the pilot in safely controlling the drone.
-
VLOS (Visual Line Of Sight operation) - operation in direct sightA UAS mode of operation in which the remote pilot is able to maintain uninterrupted and unassisted visual contact with the unmanned aircraft so that he can control its flight path to avoid collisions with other aircraft, people, and obstacles.
-
VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing)Vertical takeoff and landing
-
Thermal imaging camera
A thermal imaging camera detects infrared radiation and makes temperature differences visible. When used in drones, it enables operations at night or in poor visibility conditions—for example, for searching for people, firefighting, building inspection, or agriculture. This allows heat sources, leaks, or overheating to be detected quickly and accurately. For more information , visit DJI drone with thermal imaging camera—large selection of drones online
-
Waypoint Navigation
A flight mode in which the drone flies a predetermined route based on GPS coordinates.
-
WindVertical and horizontal air movements can have a significant influence on the operation of a UAS. Remote pilots must take this influence into account in their flight planning. On the one hand, the different air movements directly affect the flight path of the unmanned aerial vehicle. On the other hand, steering against the air movement always means higher battery consumption and consequently a sometimes considerable reduction in flight time.
-
Wind Resistance
The ability of a drone to fly stably in different wind conditions.
-
Wind Turbine Inspection
The use of drones to inspect and maintain wind turbines in order to detect damage or wear at an early stage.
-
X-Frame
Here the rotors of a drone are mounted in an X-shape.
-
X configurationMost manufacturers (DJI, Yuneec, Parrot) design multicopters as X-configurations. The motors are offset by 45° to the direction of flight so that the propellers and arms are not visible in the direction of flight when taking photos or filming.
-
X8 Configuration
A drone configuration with eight propellers arranged in an X-shape.
-
Yaw
The yaw, i.e. the control axis, allows the drone to rotate around its own axis.
-
Yuneec
A well-known drone manufacturer known for its Typhoon series.
-
Z-Axis Stabilization
Stabilization of the drone along the vertical axis to minimize camera shake and ensure stable shots.
-
Pliers
Vestibulum volutpat enim velit, a pharetra lacus interdum ac. Donec velit libero, sodales eu convallis non, auctor vitae arcu. Donec mollis varius diam, in hendrerit sapien viverra non. Nullam ac dolor quam. Maecenas vel purus ac tellus dapibus ultricies. Aliquam fermentum, lacus vitae dapibus scelerisque, arcu libero dapibus augue, quis blandit erat mauris non dolor. Nam est dolor, rutrum vel convallis eu, sodales imperdiet dui. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Morbi semper vulputate augue ut convallis. Cras ut urna vestibulum, tincidunt nisi in, venenatis massa. Proin vel ante tristique, tincidunt est et, aliquet quam. Curabitur a dui accumsan, feugiat ante rhoncus, rhoncus lorem. Pellentesque mollis dolor non est iaculis laoreet. Aliquam malesuada justo diam, nec finibus libero rhoncus lobortis.
-
Zenith
The point directly above the drone, often used as a reference point for surveying and mapping.
-
Zenmuse
Zenmuse describes various camera and sensor modules that the Chinese drone manufacturer DJI offers for sale.
-
Zero-Takeoff Weight
The weight of the drone without fuel or battery, often used to calculate the maximum payload.
-
Zoom Camera
A camera with an optical or digital zoom function that can be attached to drones to view distant objects in detail.